A simple solution for green energy storage
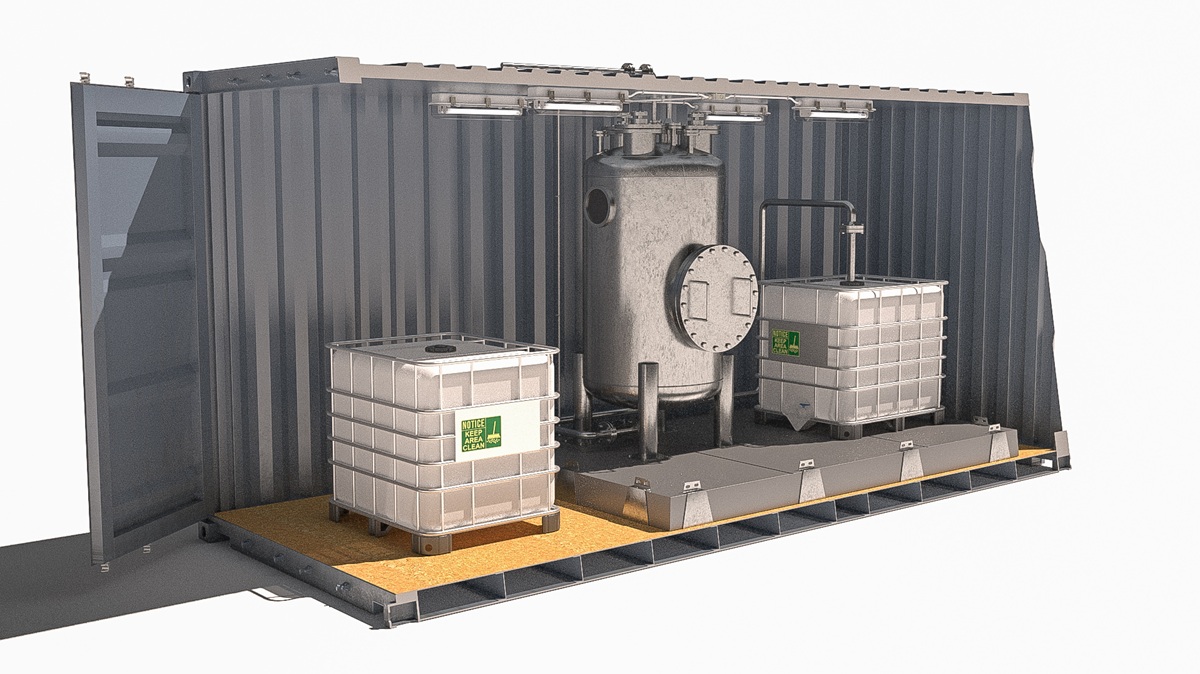
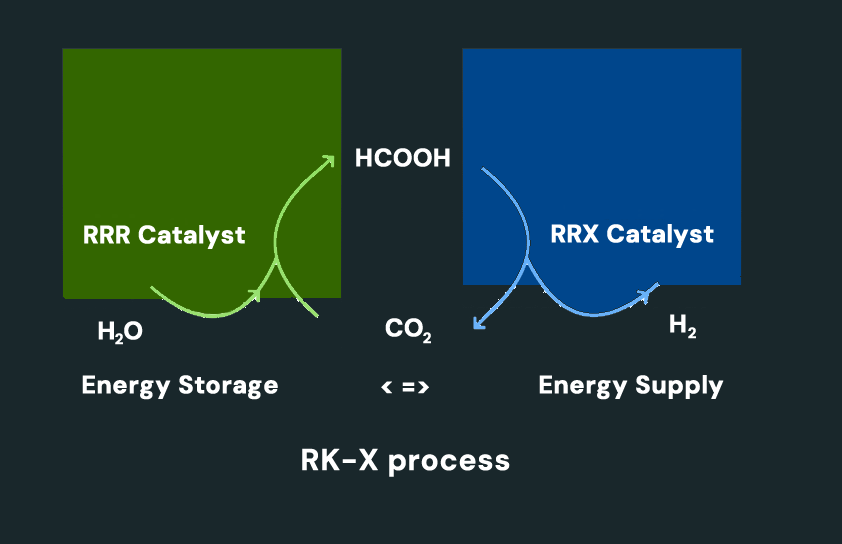
RK-X technology realizes green energy storage in two simple yet revolutionary steps. The first phase is the “storage” of energy, during which formic acid (CH₂O₂ or HCOOH) can be produced from carbon dioxide and water using the RRR catalyst. This endothermic process requires renewable energy, so the energy can be safely stored in chemical form. Formic acid is a naturally occurring, non-hazardous liquid that is easy to transport and refuel. This allows the energy to reach its place of use safely, regardless of where it is produced. The second phase is the “de-storage” of energy. Formic acid stores hydrogen in a chemical bond, which can be easily released using the RRX catalyst. This process can be carried out at room temperature, using waste heat, making it a highly energy-efficient and environmentally friendly way to produce hydrogen. With this two-step solution, RK-X technology sets new standards for the safe storage and use of green energy.
How does it work and why is this photocatalytic process more economical?
During electrolysis, two chemical bonds need to be broken, while in the case of RK-X technology, only one covalent bond needs to be broken. This results in significant energy savings: while 51.5 kWh is required to produce 1 kg of hydrogen with electrolysis, only 45.4 kWh is required with the RK-X process. Overall, this represents an advantage of about 20% compared to traditional electrolysis solutions, which could bring a breakthrough in the efficiency of hydrogen production. In the first phase of the market introduction of the RK-X process, our goal is to convert 1 million tons of carbon dioxide into 1 million tons of formic acid per year. For comparison: the current global annual production of formic acid is approximately 800,000 tons. This breakthrough is not only a quantitative leap, but also fundamentally transforms energy storage. Operating the process with green electricity creates the capacity that is needed to accelerate electromobility. The energy storage medium produced in this way enables a carbon-neutral operating model for transportation: providing sustainable propulsion for millions of electric cars, e-buses, e-aircraft and tens of thousands of ships powered by formic acid fuel.
Simple green energy storage with RK-X technology
The RK-X system lays the foundation for a forward-looking new type of technological ecosystem. Formic acid is capable of storing hydrogen produced with green technology in a completely green solution.
Solution for reducing CO2 emissions
The advantage of the RK-X process is that a high CO2 emitting plant can be sensibly and economically transformed into a formic acid production plant, with the generated CO2 becoming a raw material in a new value chain and a disruptive energy storage technological system following circular principles. For example, a current power plant that is a significant concentrated carbon dioxide emitter can use the CO2 entirely for formic acid production, thereby reducing atmospheric pollution locally and incorporating carbon dioxide as a technological raw material into an energy storage system.
RK-X technology converts HCOOH back into electricity with high efficiency.